-
Astronauts need more calories and nutrients than anyone else on Earth.
-
But packaged foods lose their nutritional value in space, so what will people eat on long space missions?
-
Scientists have found the best food for astronauts, and it’s worth trying it for yourself.
In the not-too-distant future, humans may go to Mars or beyond. These deep space trips will last quite a long time; It takes at least seven months to reach Mars with current technology.
Never mind the psychological impact it could have on astronauts’ mental health or the physical effects their bodies suffer from space radiation. Let’s talk about the basics: food.
Astronauts need to eat a lot. However, long-distance space explorers won’t be able to rely solely on prepackaged foods and vitamins as they can on the International Space Station, as some of the nutrients in these products are prone to spoilage once the process is complete. year.
Moreover, astronauts need much more energy to function than humans on Earth because microgravity affects human metabolism. A 40-year-old, 154-lb man in space, for example, might need 2,700 calories a day instead of 2,000, according to the study.
As a result, at least some of astronauts’ diets during long space missions will likely come from fresh, renewable products. grew up on a spaceship.
The perfect astronaut meal: space salad


To this end, an international team of scientists calculated 10 different crop combinations that could be grown on deep space missions and published their results in the peer-reviewed journal of the American Chemical Society. Food Science and Technology.
In their study, the researchers took into account the astronaut’s nutritional needs, how much space the crops would take up, as well as the amount of water each plant needed.
The “winning” crop combination had the best synergy between nutrition and efficient farming.
It has high vitamin levels and contains crops that grow in 50 to 100 days and take up relatively little space. And most of every plant, except the seeds, is edible.
Using only produce from winning combinations, scientists have created a vegetarian space salad recipe that I tried.
How does it taste
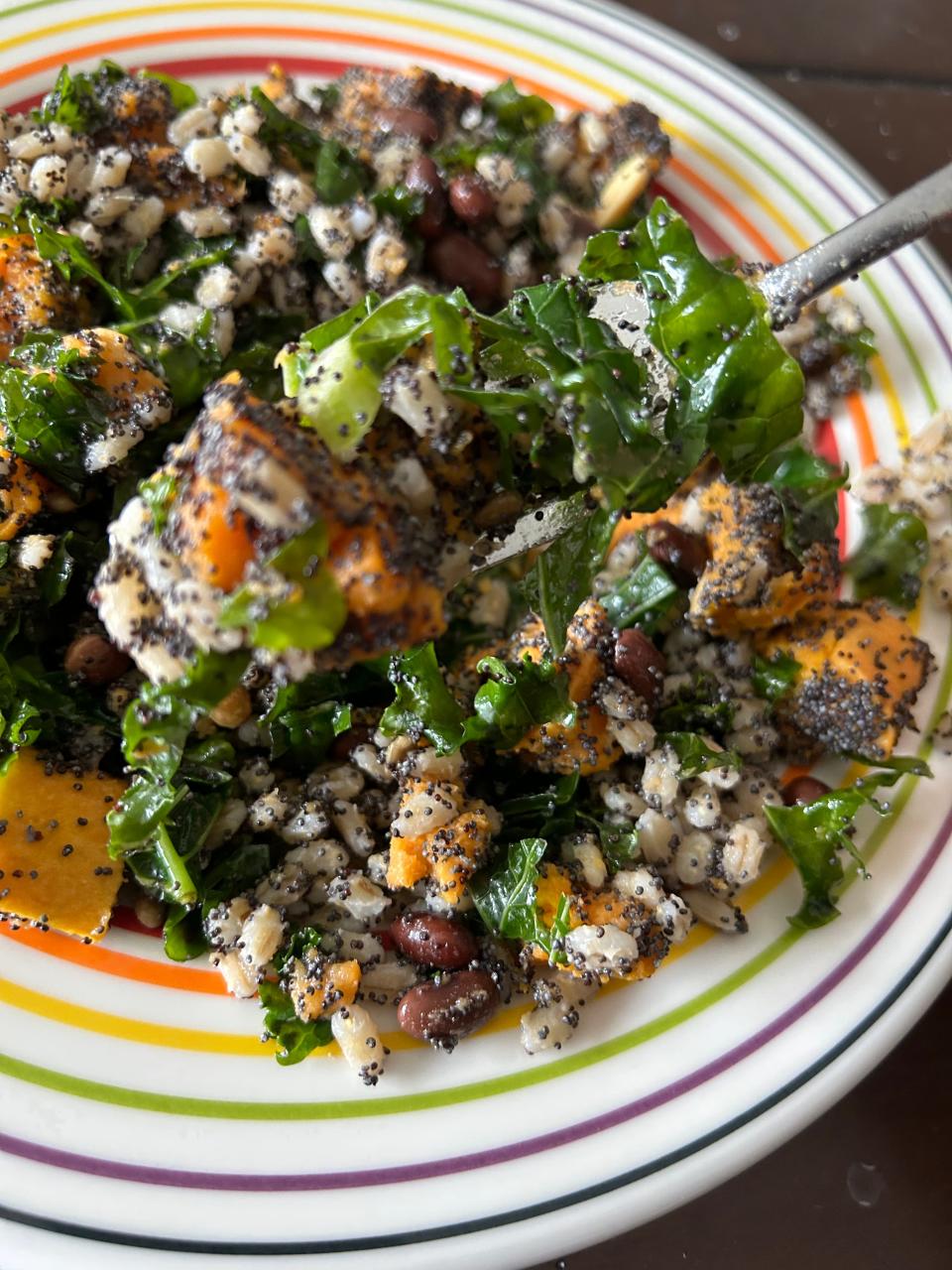
I decided to make the dish and decide for myself how to prepare this space salad of the future. I was pleasantly surprised at how delicious it was.
The recipe was designed to meet the nutritional value of three male astronauts, each offering approximately 900 calories per serving. According to the research, here is a list of the ingredients.
You will need:
-
642 grams sweet potatoes (about 5 small potatoes)
-
223 grams pearl barley (about 1 cup)
-
155 grams of poppy seeds
-
79 grams of cabbage
-
63 grams of soybeans
-
25 grams of peanuts
-
18 grams of sunflower seeds
Study co-author Volker Hessel, professor of sustainable chemical engineering at the University of Adelaide, said an astronaut should ideally eat this meal once a week as part of a meal rotation.
I could definitely see myself eating space salad that often. The salad was very easy to make and took about 30 minutes from preparation to plate. Plus all that protein filled him up.
Long space flights require special diets


The study’s authors developed the space salad based on the following: NASA’s nutrition guidelines using computers to calculate the most nutritious, resource-efficient combination for long space travels. Business Insider reached out to NASA’s Space Food Systems Laboratory for comment but did not respond.
To prevent astronauts’ skeletons from melting in zero gravity, in addition to more energy, astronauts will also need more of certain vitamins, such as calcium and magnesium. They will also need potassium for homeostasis, which balances and stabilizes all the body’s systems.
Now thank God Research from the International Space Station suggests that the nutritional content of crops grown in space is generally close to that of their Earthly cousins.
Therefore, we can approximately calculate how much nutrition astronauts would gain from eating this space salad.
For example, one serving of space salad contains:
-
52 g of poppy seeds contain 749 mg of calcium (62% of the recommended daily intake for astronauts)
-
214g sweet potatoesOffers 807 mg potassium (17% of the DV)
-
74 g barley providing 16 mg magnesium (4% of daily intake)
But of course, not every astronaut will need exactly the same diet.
Future Research


The scenarios in the study were designed only for male astronauts. Female astronauts will likely have different needs for nutrients such as magnesium and iron.
Therefore, the authors said they plan to adjust the diet plans to include female astronauts in future studies.
Making matters even more difficult, Hessel said each team member’s body will respond differently to the stresses of space.
Additionally, the astronaut’s nutritional needs may change during the journey.
For example, when an astronaut spends an hour outside the ISS performing an extravehicular activity, NASA 2020 nutrition rules We recommend that they eat an extra 200 calories that day.
The computer simulations in the study should be able to create new diets when necessary. “We can make recommendations for new requirements almost the same day,” Hessel said. But a shuttle’s food supply will need to be flexible enough to account for these changes.
What about meat?
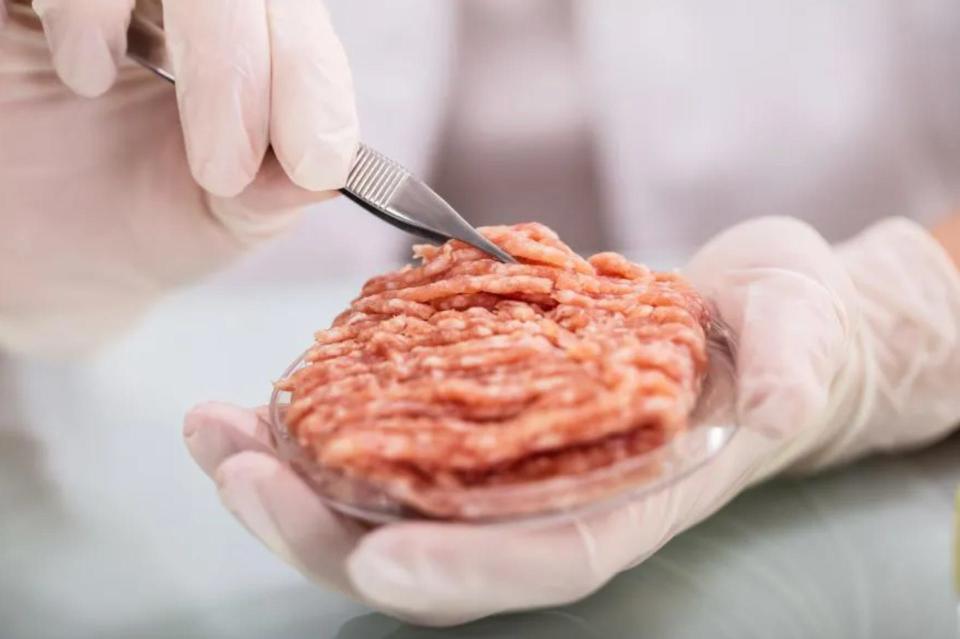


Meat lovers need not worry: The future of space doesn’t have to be vegetarian. Past astronaut meals have included seared shrimp cocktail, beef brisket, and even teriyaki chicken.
Future space explorers could also eat lots of lab-grown meat, which is currently in the middle of the FDA approval process and will soon be available in restaurants.
Scientists are also working on it raising fish in space so that astronauts can eat fresh meat. Fish could be an ideal part of the space ecosystem, the study authors say, as astronauts can feed them excess plant material and then collect their feces for fertilizer.
If you want to add meat to your space salad, I recommend pairing it with a lighter option like chicken or tuna. However, if your astronaut heart desires to explore further, you can try any salad additions you like.
Read the original article on Business Insider