Shape of the asteroid dimorphos Changed at NASA’s request DARTS GAME The spacecraft deliberately crashed into it in 2022 as part of testing humanity. planet defense Abilities.
DART, the Double Asteroid Redirection Test, was designed to see if we could redirect a potentially hazardous asteroid away from us. Soil. Sent to one person binary asteroidWhere the 170-meter-wide (560-foot-wide) Dimorphos orbits a larger 760-meter-wide (2,493-foot-wide) space rock called Didymos. When DART hit Dimorphos on September 26, 2022, astronomers were able to measure how much the impact pushed the asteroid by measuring how the space rock’s orbit around Didymos changed.
But now scientists have shown that DART isn’t just pushing Dimorphos; it also hit Dimorphos with enough kinetic energy to reform it.
Relating to: NASA’s asteroid impact completely changed the shape of the DART mission target
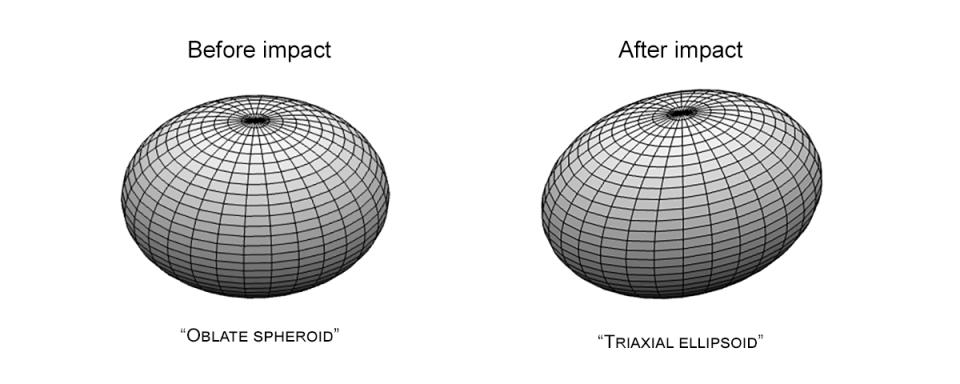
“The entire shape of the asteroid changed from a relatively symmetrical object to a ‘triaxial ellipsoid,’ something that looked more like a rectangular watermelon,” said NASA’s Shantanu Naidu. Jet Propulsion Laboratory (JPL) one expression.
Originally Dimorphos would have been a flattened spheroid resembling a crushed ball. DART’s impact at 5 kilometers per second (3 miles per second) sent shock waves through the asteroid, causing it to elongate further and shift its spin axis off-center. The new shape is understood by astronomers from the light curve of the Didymos-Dimorphos system; this curve is aligned in such a way that we can see them transitioning and shadowing each other.
This conclusion from Naidu’s team is also shared in a study published in February by a group led by Sabina Raducan from the University of Bern in Switzerland. Raducan’s team reached the conclusion The impact resulted in the ejection of up to 1% of Dimorphos’ mass. spaceand the other 8% is redistributed to the surface as the asteroid absorbs the energy of the impact and reforms itself. The result was that Dimorphos had to be a loose pile of rubble to allow him to shapeshift in this way; a pile of dirt and rocks held together by weak forces. gravity and unlike a solid structure that can be easily reshaped, it does not bend easily.
“Results [Naidu et al’s] “This study agrees with other published studies,” said Tom Statler, the study’s lead scientist. solar system small sizes NASA Headquarters is in Washington DC. “Seeing separate groups analyze data and independently come to the same conclusions is the hallmark of a sound scientific conclusion.”
The new study also confirms how much Dimorphos’ orbit around Didymos has changed due to the impact of DART. Before the collision, Dimorphos orbited Didymos every 11 hours and 55 minutes, with an orbital radius of 1,189 kilometers (3,900 feet).
Light curve studies and radar observations Deep Space NetworkThe Goldstone Solar System Radar in California shows Dimorphos’ orbital period reduced to 11 hours 22 minutes 3 seconds, with a margin of error of 1.5 seconds. The orbital radius also dropped to 1,152 kilometers (3,780 feet). Given that Dimorphos’ spin axis is now deviated from its geographic center, Dimorphos now swings back and forth as it orbits Didymos; this is a swinging motion that can be detected through the shape of the light curve.
“Before I affect the times [transit] “The events occurred regularly and showed a circular orbit,” said JPL’s Steve Chesley. “There were very slight timing differences after impact, indicating that something was askew. We never expected to get this kind of accuracy.”
DART was designed to test whether it would be possible to change the orbit of a small but dangerous asteroid if it were on a collision course with Earth. The experiment exceeded scientists’ expectations in terms of how hard DART nudged Dimorphos and what the impact taught us. asteroids Act when faced with this type of kinetic violence.
Related Stories:
— Asteroid impact: Here’s the last thing NASA’s DART spacecraft saw before impact
— James Webb, DART asteroid crash seen by Hubble space telescopes (photos)
— DART impact gave asteroid Dimorphos a tail of debris thousands of kilometers long (striking photo)
“DART not only shows us the path to asteroid deflection technology, it also reveals a fundamental new understanding of what asteroids are and how they behave,” Statler said.
Didymos and Dimorphos’ work is not finished yet. In October 2024, European Space Agency In addition to studying the nature of asteroids more closely, it will launch the Hera spacecraft on a mission to encounter two asteroids and examine how much damage DART has done to Dimorphos.
The new results were announced on March 19. Planetary Science Journal.