Editor’s Note: A version of this story appeared in CNN’s Wonder Theory science newsletter. To get it in your inbox, Sign up for free here.
Humans landed on the moon during NASA’s Apollo program in the late 1960s and 1970s using computers with much less processing power than today’s smartphones.
Still, even fifty years later, landing on the moon is no easy feat.
Several major missions over the past few years have proven this point: Israel’s Beresheet spacecraft crashed into an ancient lunar volcanic field called the Sea of Serenity in 2019, and Russia’s Luna-25 mission and a commercial Japanese lander called Hakuto-R crashed into the moon’s surface last year. hit. (However, India did celebrate becoming the fourth country to land a spacecraft on the moon.)
Whether successful or not, these efforts are part of a new space race, with efforts to explore the Moon at the forefront. Many projects are expected to move towards the moon with a soft landing this year.
The plane, which made the first flight on a commercial mission outside the United States, did not go as planned.
discoveries
Astrobotic Technology, the Pittsburgh-based company developing the first U.S. lunar lander to be launched in fifty years under a $108 million contract with NASA, has abandoned plans to attempt a soft landing on the moon by Peregrine Mission One.
The spacecraft successfully lifted off Monday atop the Vulcan Centaur rocket, a new vehicle developed by United Launch Alliance that is on its inaugural flight. Shortly afterwards, Peregrine suffered “critical” fuel loss due to a fuel leak; This means that a controlled moon landing, originally planned for February 23, is off the table, according to Astrobotic.
NASA had hoped that Peregrine 1 would be an early success for its Commercial Lunar Payload Services program, which aims to reduce the cost of building a lunar lander, especially at a time when the space agency is facing long delays in sending astronauts back to the moon.
discoveries
Northern Europeans are among those most prone to the debilitating autoimmune disease multiple sclerosis, and a new study based on DNA extracted from ancient bones and teeth offers clues as to why.
A comparison of more than 1,000 ancient genomes compiled as part of a new database found a link between multiple sclerosis risk and a common ancestor with a group of Bronze Age nomadic herders known as the Yamnaya.
Researchers believe these nomads from the Central European steppes moved westward and introduced a genetic variant that protected against infectious pathogens once carried by domesticated animals but evolved to affect modern diseases in a very different way.
dig this


What caused the extinction of the largest apes that ever lived?
New research published this week has shed more light on the mystery of why Gigantopithecus blacki, a primate species sometimes called the real King Kong because it was almost 10 feet long, disappeared.
Paleontologists analyzed and dated fossils and sediments from caves where animal remains were found; Thus, they understood how the nutrition of animals and the environment in which creatures live changed over time, narrowing down a possible time period and the cause of species extinction.
Gigantopithecus was discovered in 1935 after paleontologist GHR von Koenigswald found the large teeth being sold as “dragon bones” at a traditional medicine shop in Hong Kong.
All Over the Universe
The first fast radio burst, or FRB, was discovered in 2007, and since then scientists have detected hundreds of intense, millisecond-long bursts of radio waves coming from distant parts of the universe.
Much about these fast, cosmic flashes and their origins remains unknown. But now astronomers have traced one of the most powerful and farthest fast radio bursts ever detected to its unusual cosmic home: a rare group of “blob-like” galaxies.
The unexpected discovery could provide insight into what causes mysterious bursts of radio waves, a question that has baffled scientists for years.
Once upon a time a planet
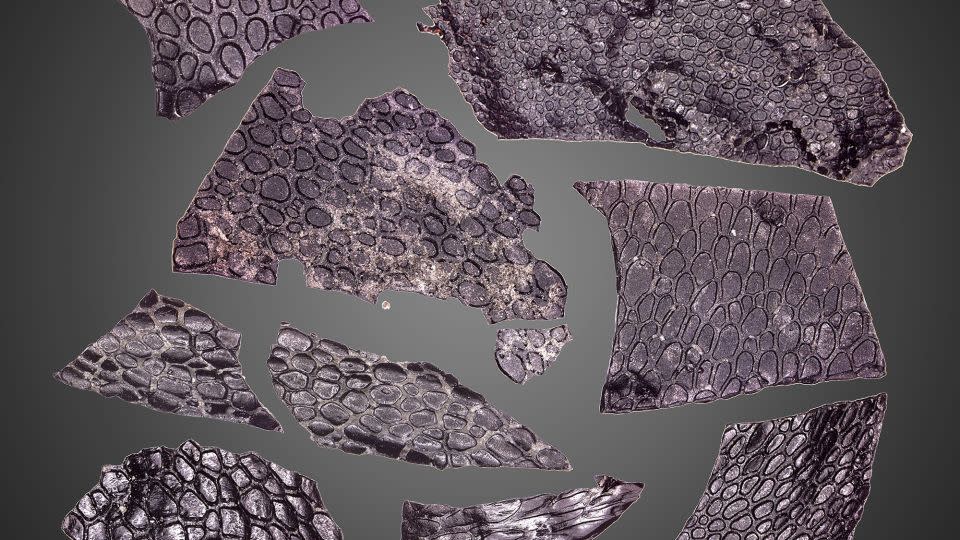


The world’s oldest known fossilized skin belonged to a species of reptile that lived before dinosaurs roamed the Earth.
The piece of skin, which has a pebbly surface reminiscent of crocodile scales, is more than 289 million years old, according to a new study published Thursday. That is, it is at least 130 million years older than the oldest known skin fossil.
Skin and other types of soft tissue rarely fossilize because they decay much more easily than bone.
But researchers at the University of Toronto Mississauga believe this specimen’s location has been preserved because of its unique features: the Richards Spur limestone cave system in Oklahoma, where many of the oldest examples of early land animals were found.
curious things
Watch out for these remarkable stories:
— China, in partnership with the European Space Agency and other institutions, has launched a probe that will investigate X-ray bursts from black holes and other high-energy space phenomena.
— Norway could become the first country to allow deep-sea mining despite growing concerns from scientists and environmentalists.
— A 106-year-old three-masted sailing ship is embarking on a two-year voyage that retraces British naturalist Charles Darwin’s pivotal voyage that inspired the theory of evolution.
— An older, same-sized relative of T. rex has just been identified in New Mexico, according to researchers.
Did you like what you read? But there is more. Sign up here To get the next edition of Wonder Theory brought to you by CNN Space and Science writers in your inbox Ashley Strickland And Katie Hunt. They are finding wonders on planets beyond our solar system and discoveries from the ancient world.
For more CNN news and newsletters, create an account at CNN.com