Mars experienced a sudden break in the cosmic order about a year ago. It was as if the red planet had briefly been transported to another solar system.
Normally in our solar system, the sun constantly emits a stream of charged particles and magnetic fields called the solar wind.


This wind washes over planets and puts pressure on them that helps hold them in their atmospheres. It also interacts with their atmospheres, creating auroras (colorful northern lights often seen on Earth).
However, in December 2022, the solar wind around Mars suddenly disappeared, resulting in the planet’s atmosphere swelling by thousands of kilometers.
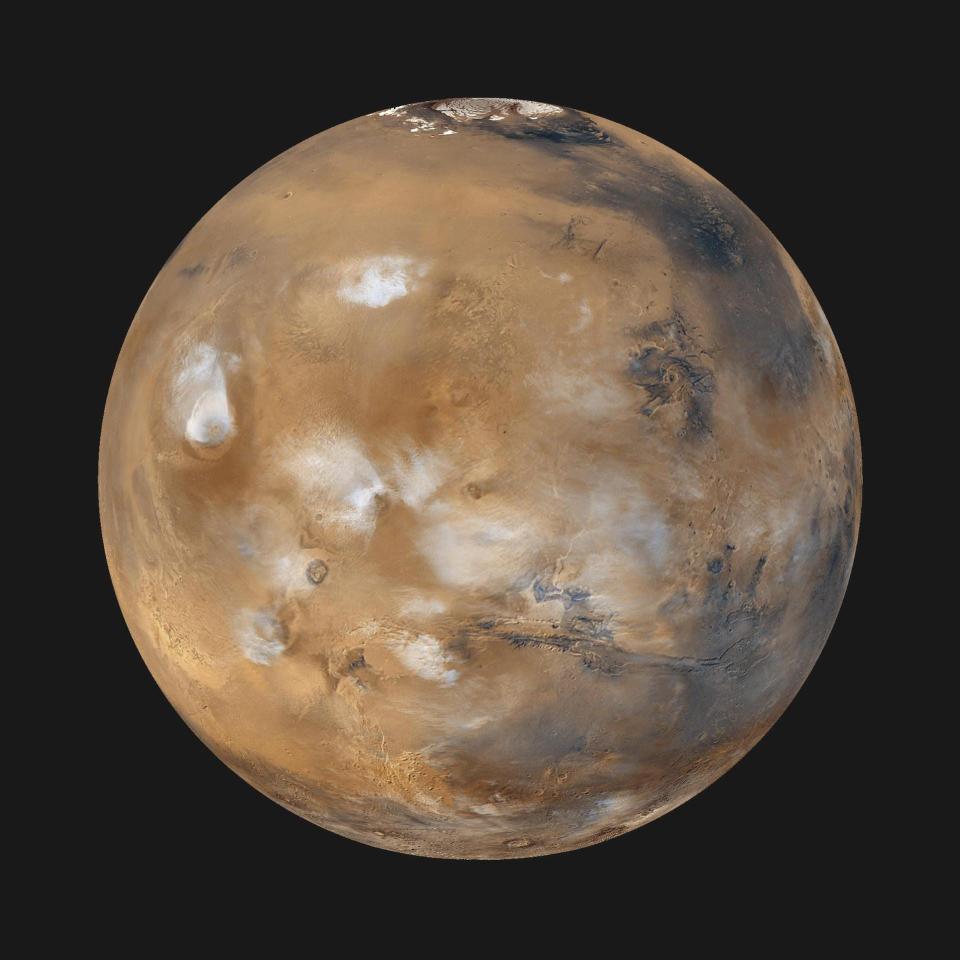


NASA’s MAVEN spacecraft orbiting Mars observed it all. Scientists announced their discovery of the event on Monday at the fall meeting of the American Geophysical Union in San Francisco.
Solar explosion wiped out solar wind
Scientists have determined that the Sun is emitting a high-speed burst of solar wind that sweeps away a region of the normal solar wind and leaves a gap behind.
“Every solar storm is different, but this one is even more different,” Shannon Curry, principal investigator for the MAVEN mission, said at the briefing.
According to MAVEN’s data, there was almost no solar wind on Mars; The density of solar particles had decreased by a factor of 100. As a result, Mars’ atmosphere swelled by thousands of kilometers.
NASA scientists said this unusual phenomenon was last seen in 1999, when a NASA satellite observed that the solar wind had effectively disappeared around Earth, causing our own planet’s atmosphere to swell five times more than normal.
Mysterious incident may offer clues in search for alien life


NASA scientists were driven to investigate this rare, extreme event for several reasons.
For one, “understanding solar phenomena is going to be really important for human exploration on Mars,” Curry said.
This is because Earth’s atmosphere protects us from the sun’s tricks, but astronauts in space are vulnerable to the extreme radiation that can come with solar flares.
NASA plans to one day send humans to Mars, which would expose them to the solar wind and radiation for longer periods of time. According to Popular Science’s report, this journey will take a total of two to three years. By comparison, NASA astronauts typically stay on the International Space Station for only six months, and the longest recorded human spaceflight was 437 days.
The vanishing solar wind also offers clues as to how Mars became such a dry, harsh and lifeless place.
The planet used to be filled with water, and scientists suspect microbial life may have existed on Mars at that time. But Mars’ atmosphere shrank into space, eventually leaving it very cold and exposed to liquid water.
Strong solar wind dams may have eroded the Martian atmosphere, Curry said. To understand whether this is what is happening, it is useful to examine the opposite extreme, where the solar wind disappears.
There’s another reason for alien life to understand the disappearance of the solar wind: The event offers a glimpse of how rocky planets might appear around other, less windy stars.
Mars’ magnetic profile has also changed
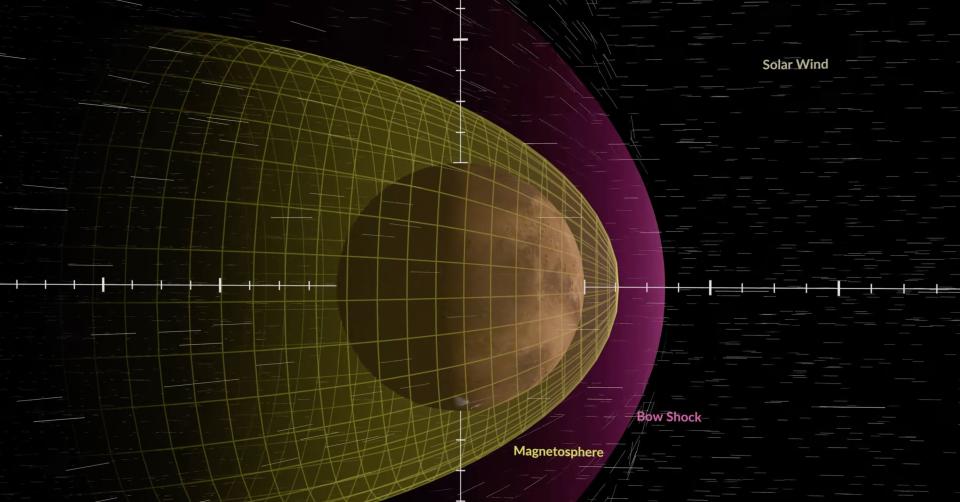

The solar wind also interacts with the planet’s upper atmosphere, forming its magnetosphere (the region of space dominated by Martian magnetic fields).
Like Earth, the magnetosphere surrounding Mars acts like a bubble around which the solar wind must flow.
But when the solar wind disappeared, the magnetosphere ballooned outward, engulfing the entire orbit of the MAVEN spacecraft.
Just as the solar wind disappeared on December 25, 2022, it returned on December 27, 2022, and Mars’ atmosphere and magnetosphere returned to their normal proportions.
As the Sun becomes more active, rarer events like this may occur


The Sun is approaching the peak of its 11-year cycle, which means its bubbling plasma surface is forming more sunspots and emitting more outbursts, solar wind floods, and other extreme events.
On Earth, we know that solar flares and solar storms can create beautiful aurora borealis, cause magnetic damage that disrupts compasses, knock satellites out of orbit, and even block radio signals and interfere with power grids.
Next year, as the sun’s activity continues to peak, NASA’s MAVEN mission may have more opportunities to study such solar flares from a Martian perspective.
Read the original article on Business Insider